Description
ETAP announces the latest version of its power system analysis software, ETAP 16.2. This point release includes several new enhancements and general improvements. It is now easier for ETAP customers to experience the powerful features and capabilities of ETAP’s Renewable modules.
The following features are part of the ETAP Base Package configuration:
- Model and simulate wind farm operation with grid control
Wind Turbine Generator
Model, Analyze & Study Impact of Onshore & Offshore Wind Turbine Generator on Electric Power GridETAP Wind Turbine Generator is used to model and simulate wind turbine power generation and operation under steady-state and dynamic conditions.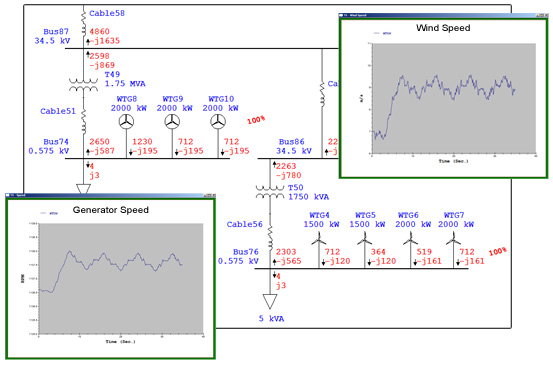
ETAP Wind Turbine Generator includes two approaches for studying wind power systems when combined with the appropriate network analysis capabilities and simulation scenarios:
- Design & Analyze Wind Farms or Wind Parks
- Wind Power Integration Impact on Transmission Grid
Wind Turbine Generator Software Key Features
- Model unlimited wind turbine generators individually or in groups
- Short-circuit modeling per IEC 60909-2016 *
- Crowbar & current limit short circuit model with active & reactive *
- Auto-trip voltage & duration for Low-Voltage Ride Through (LVRT) *
- Detailed modeling of turbine dynamics including aerodynamics & power coefficients
- Fully integrated with ETAP User-Defined Dynamic Model (UDM)
- Generic dynamic models for grid interconnection based on IEC 61400-27-1-ed1 *
• Type 4A• Type 4B
* Upcoming release
- Generic dynamic models for grid interconnection based on WECC
• Type 1• Type 2• Type 3• Type 4
- User-defined wind turbine manufacturer and model library
- Include vendor specific dynamic model for simulation or utilize generic models for grid interconnection studies
- Simulate transient wind conditions with ramp, gust, & noise disturbances
- Create multiple wind categories for predictive “what if” studies & scenarios
- Perform transient stability analysis with individual or zone-based disturbances
Design & Analyze Wind Farms or Wind Parks
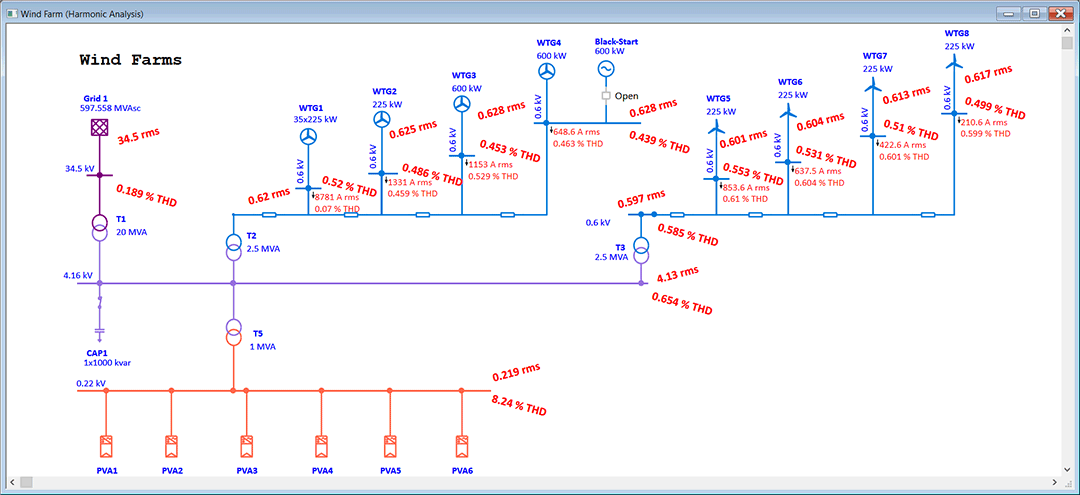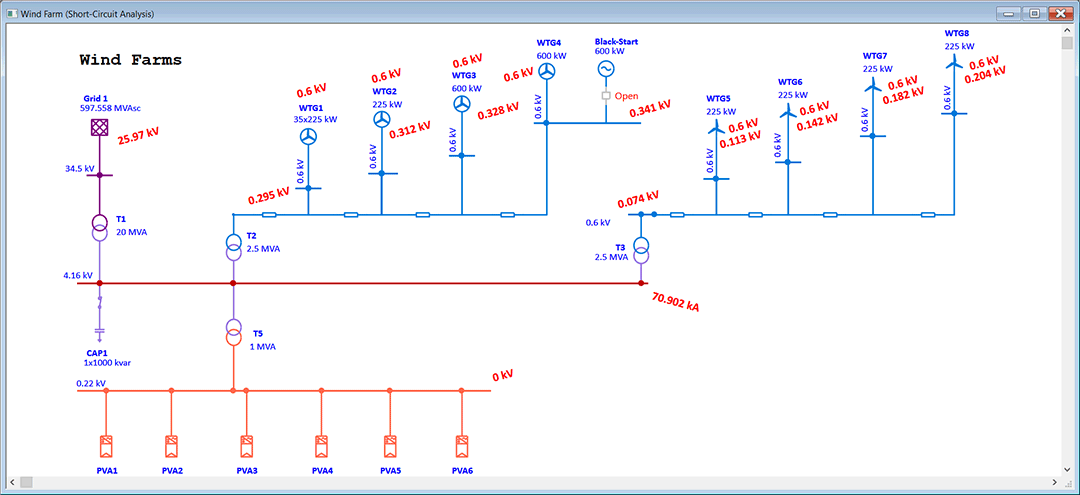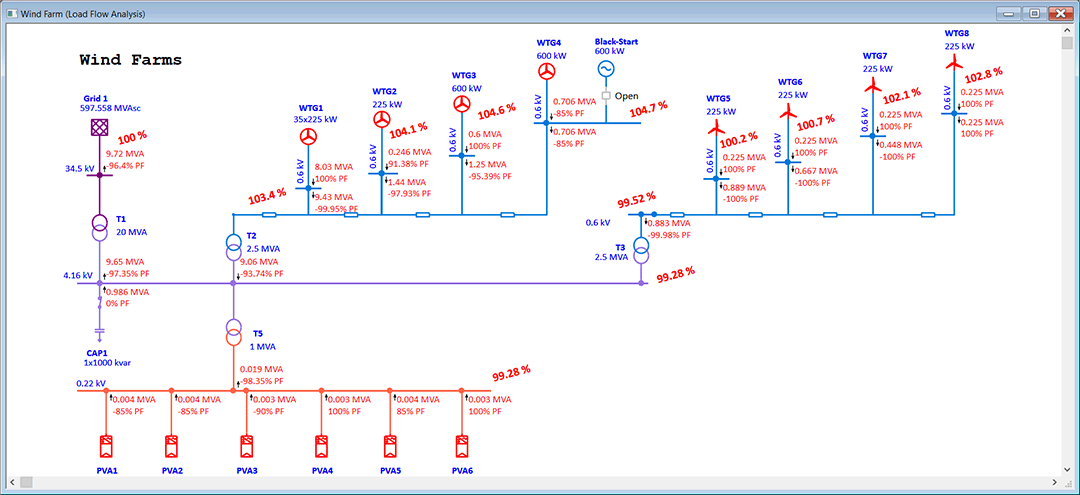
Wind farm designers or planners can model and simulate wind turbine generators using any technology type, design wind power collector systems, size underground cables, determine adequacy of system grounding, and more. Access of engineering device libraries for wind turbine generator, cables, protection relays, overhead lines, etc. make the design process flexible yet efficient.
Wind Power Integration Impact on Transmission Grid
System planners can represent wind turbine generator as a single machine mathematical model of the entire wind farm to understand the impact of wind penetration in the grid under variability of wind.
System dynamic behavior can be studied by changing wind speed (gust, ramp), tripping the wind plant, simulating system faults at wind turbine or grid connected buses. Study results determine extent of system vulnerability with increase in penetration and uncertainty of wind power generation. User-defined actions may be added to simulate wind turbine and grid transient recovery variations and relay operations. It also predicts the dynamic response of each individual wind turbine generator.
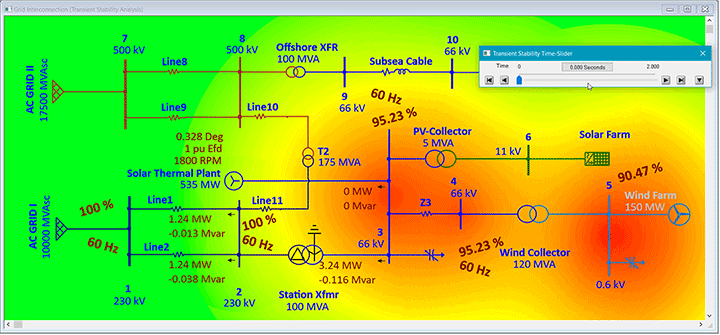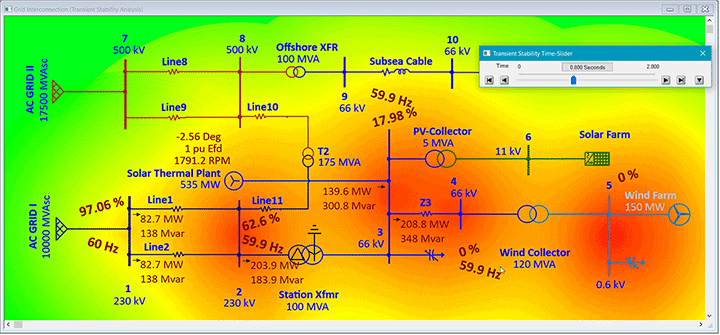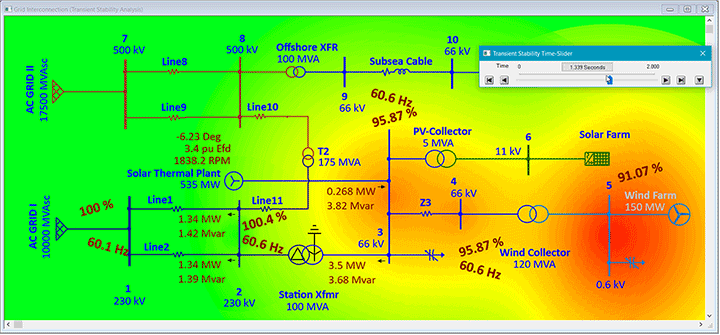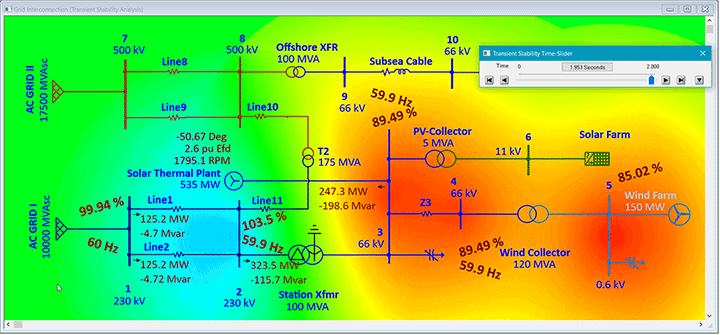
ETAP Wind Generation Solution
ETAP Wind Turbine Generator can be used to verify grid connection compliance, steady-state and dynamic simulation of whole wind parks, size collector systems, calculate short circuit current levels, analyzing alternative turbine placement, tuning of control parameters, selection and placement of protective devices, and more.
- Intelligent Geospatial Diagram
- Time-Series Unified AC & DC Load Flow
- Short Circuit
- Dynamics & Transients
- Harmonic Analysis
- Protective Device Coordination
- ETAP Real-Time & Microgrid
- System Safety & Grounding
- Cable Sizing & Underground Raceway Systems
- Transformer Sizing & Tap Optimization
Generic Models for Wind Turbine Generators
There are presently two major industry groups working towards the development of generic models for use in power system simulations for wind turbine generators – the Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) Renewable Energy Modeling Task Force (REMTF) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Technical Committee (TC) 88, Working Group (WG) 27.
In general, the most commonly sold and installed technologies in today’s market (both in the US and overseas) tend to be the type 3 and 4 units. All the major equipment vendors supply one or both of these technologies. There are, however, large numbers of the type 1 and 2 units in service around the world, and so modeling them is also of importance. Some vendors do still supply the type 1 and 2 turbines as well.
ETAP includes wind turbine models developed by the WECC Modeling & Validation Working Group & IEC Technical Committee Working Group. These models were developed for analyzing the stability impact of large arrays of wind turbines with a single point of network interconnection. Dynamic simulations have been performed with these models, and comparisons made with results derived from higher-order models used in manufacturer-specific representations of aero conversion and drivetrain dynamics.

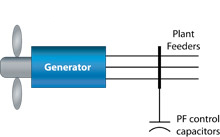
Type 1
The machine is a pitch-regulated, and drives a squirrel cage induction generator which is directly coupled to the grid. The generic model consists of generator model, drive train model and pitch controller.
Type 2
The machine operates with variable slip. It utilizes a wound rotor induction generator whose rotor winding is brought out via slip rings and brushes. An external rotor resistance is electronically modulated to effect dynamic changes in the machine’s torque-speed characteristics. The generic model includes generator model, external resistance controller, drive train model and pitch controller.
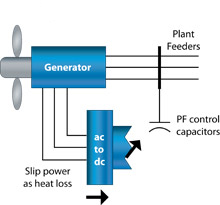
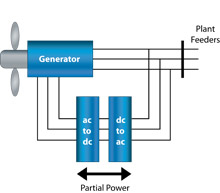
Type 3
The machine is a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG), or partial conversion. The turbine is pitch-regulated and features a wound rotor induction generator with an AC/DC/AC power converter connected between the rotor terminals and grid. The generator stator winding is directly coupled to the grid. The power converter in the rotor circuit allows for independent control of generator torque and flux, providing fast active and reactive power control over a wide range of generator speeds.
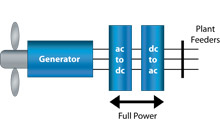
Type 4
The turbine is pitch-regulated and features an AC/DC/AC power converter through which the entire power of the generator is processed. The generator may be either induction or synchronous type. The power converter allows for independent control of quadrature and direct axis output currents at the grid interface, providing fast active and reactive power control over a wide range of generator speeds.
- Model unlimited solar panels individually or in groups to form a solar array
Photovoltaic Array / Solar Panel
Photovoltaic Array Analysis Software
Model, Analyze & Study Impact of Solar Farms on the Electric GridPhotovoltaic (PV) array comprising of solar panels are the predominant power generation components of renewable distributed energy resources (DER), solar farms with grid tied inverters, islanding microgrids, and smart grids. PV array converts solar radiation energy into direct current using semiconductors and then to alternating current electric power through inverters.

ETAP Renewable Energy module includes three methods for studying photovoltaic power systems when combined with the appropriate network analysis capabilities and simulation scenarios:
- Design & Analyze Solar Farms
- Photovoltaic Integration Impact on Transmission Grid
- Photovoltaic Impact on Distribution Grid as Distributed Energy Resource
PV Array & Solar Panel Software Key Features
- Model unlimited solar panels individually or in groups
- Series and/or parallel connection combinations to form a solar array
- User-defined solar panel library with P-V & I-V characteristic
- PV inverter dynamic modeling using ETAP User-Defined Dynamic Model
- Use Solar Irradiance Calculator to determine irradiance based on specified date, time & location
- Combine solar irradiance patterns with Time Series Unified AC & DC Power Flow to simulate daily, monthly or yearly power injection from a PV farm & PV parks
- Create multiple solar irradiance categories for predictive “what if” studies & scenarios
- Built-in inverter model eliminates the need for unnecessary node connections
- Includes modeling of Inverter Maximum Peak Power Tracking (MPPT) controller
Design & Analyze Solar Farms
Solar designers or planners can model and size, discrete solar photovoltaic panels, grid connected inverters, solar combiners and collector systems, system grounding, and more.
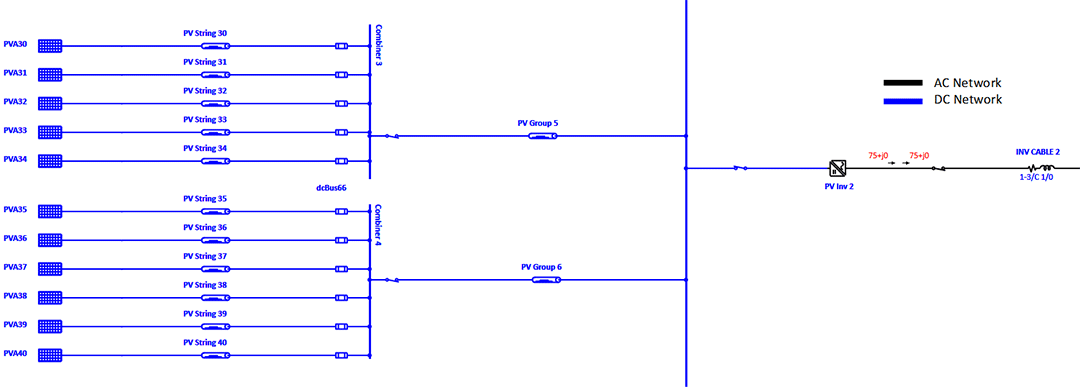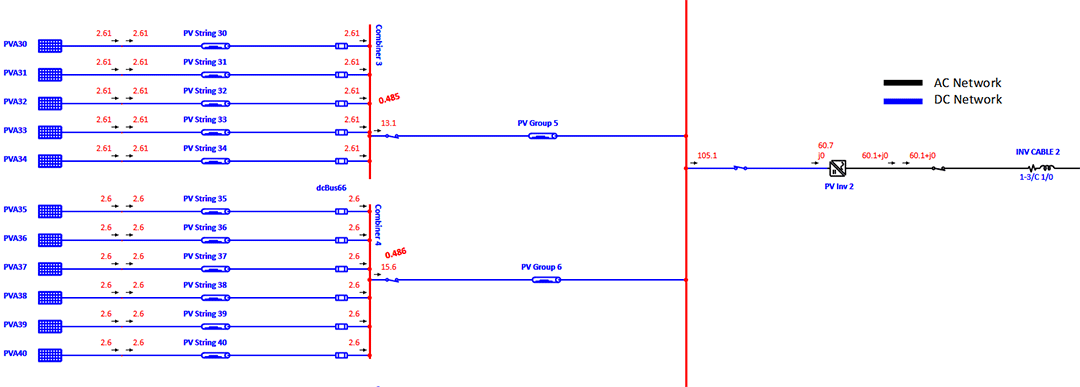
PV Integration Impact on Transmission Grid
System planners can represent solar plant as a single machine mathematical model of PV (Photovoltaic) array to understand the impact of PV penetration in the grid under varying solar and temperature conditions.
System dynamic behavior can be studied by changing solar irradiance, tripping the PV plant, simulating system faults at PV connected buses. Study results determine extent of system vulnerability with increase in penetration and uncertainty of PV power generation.
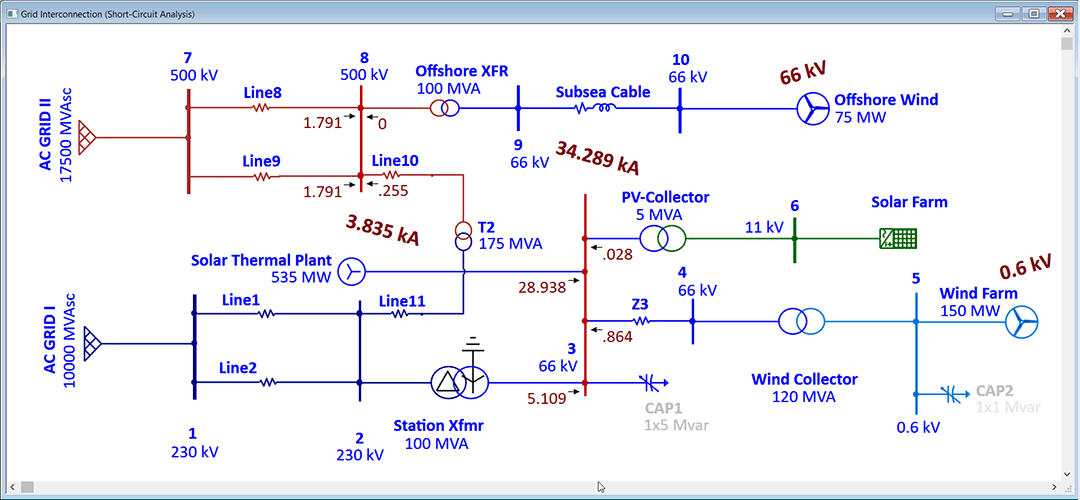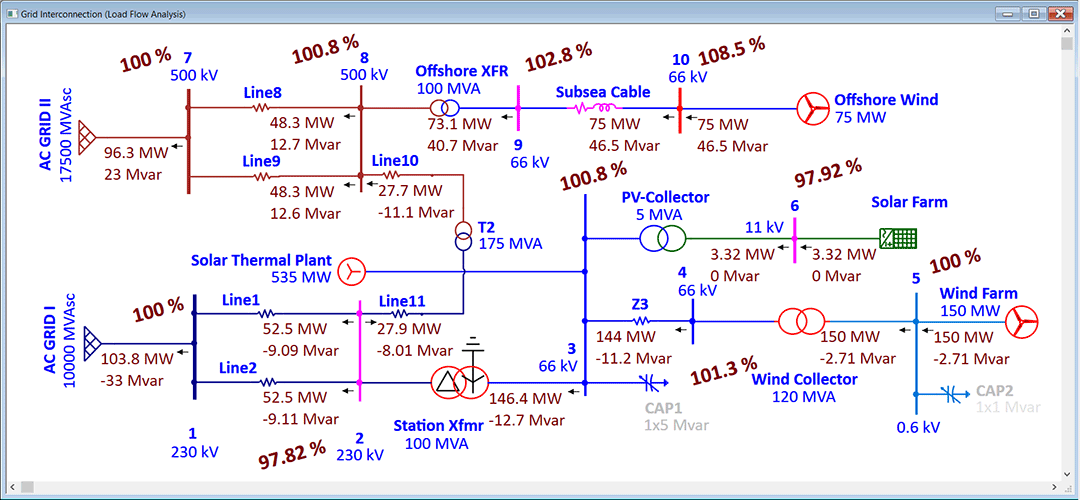
PV Impact on Distribution Grid as DER
In today’s modern grid, the penetration of solar generation has a noticeable impact on distribution networks. Distribution system planners can utilize ETAP PV Array combined with a suite of analysis modules and Intelligent Geospatial Diagram to study impact of rooftop solar or generation hosting capacity of the feeder in addition to its load hosting capacity.
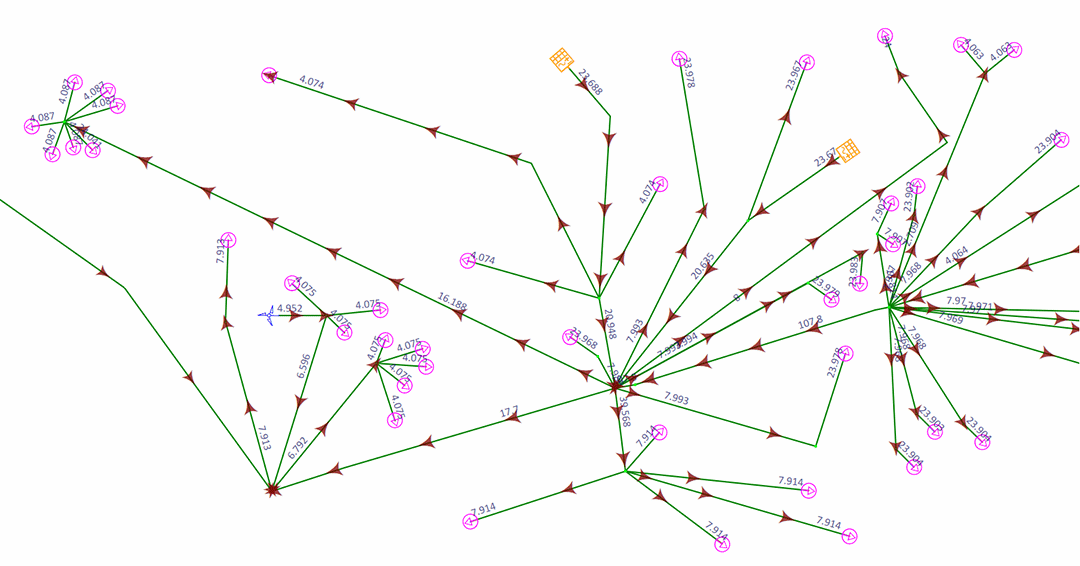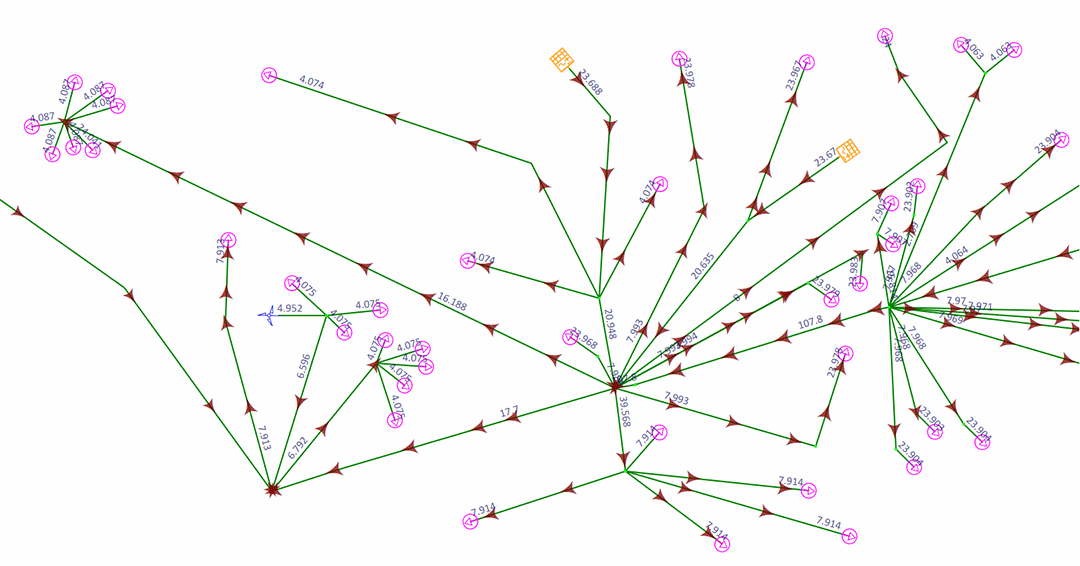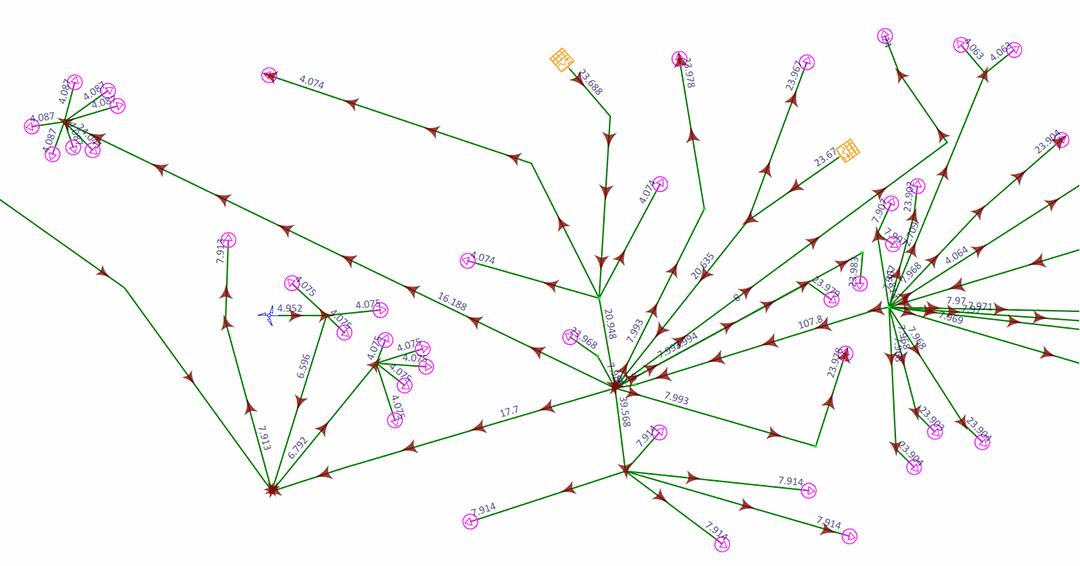
ETAP PV Array & Solar Panel Solution
Photovoltaic Array and Solar Panel elements are part of the Renewable Energy module and integrated with ETAP calculation modules and visualization foundations including:
- Intelligent Geospatial Diagram
- Time-Series Unified AC & DC Load Flow
- Short Circuit
- Dynamics & Transients
- Harmonic Analysis
- Protective Device Coordination
- ETAP Real-Time & Microgrid
- System Safety & Grounding
- Cable Sizing & Underground Raceway Systems
- Transformer Sizing & Tap Optimization
PV Array & Solar Panel Modeling
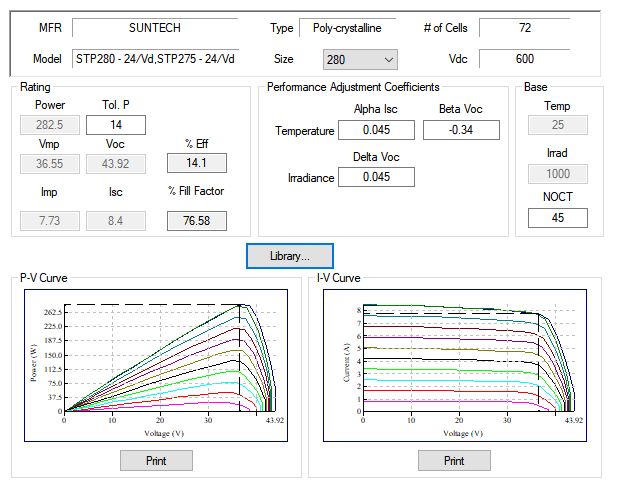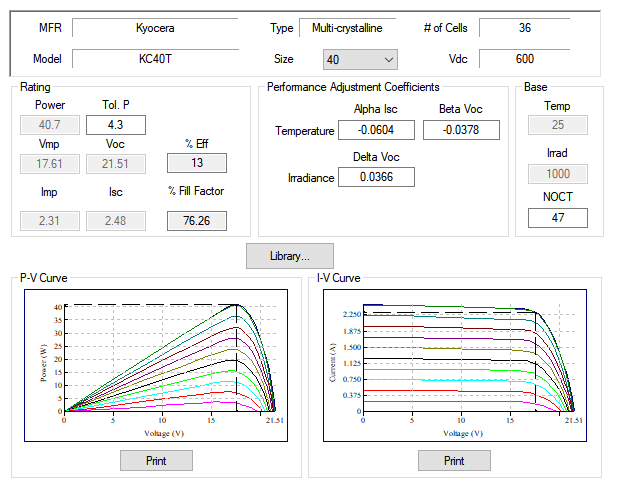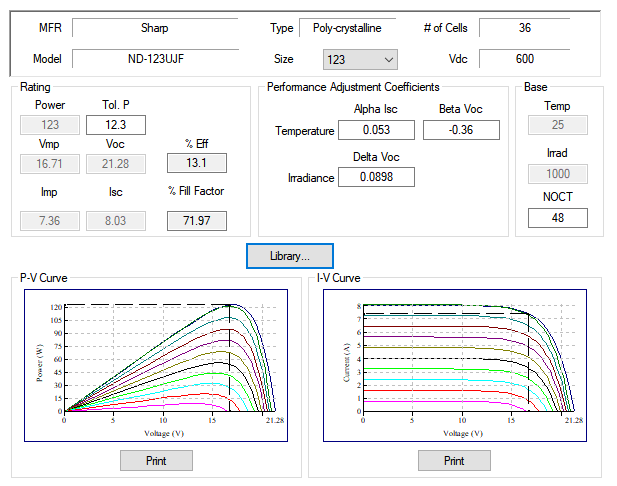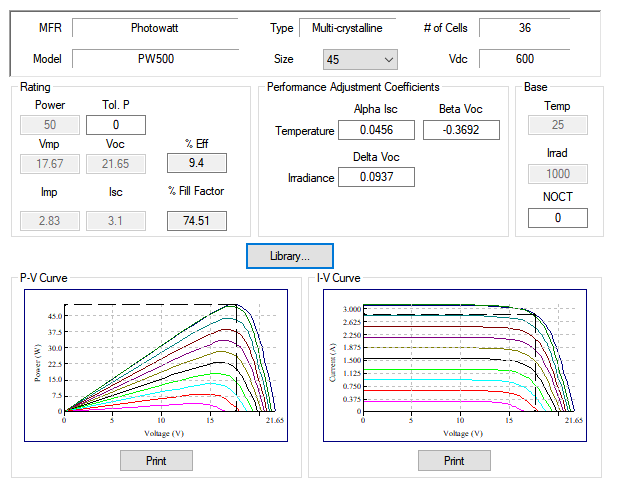
Photovoltaic characteristics including P-V and I-V curves are defined in the user-configurable ETAP Photovoltaic Library or specifying the maximum peak power voltage (Vmpp), maximum peak power current (Impp), open circuit voltage (Voc) and short circuit current (Isc).
ETAP considers the effect of performance coefficients (α, β, γ) that define anges in irradiance and cell temperature to automatically calculate the expected power output from the photovoltaic array.
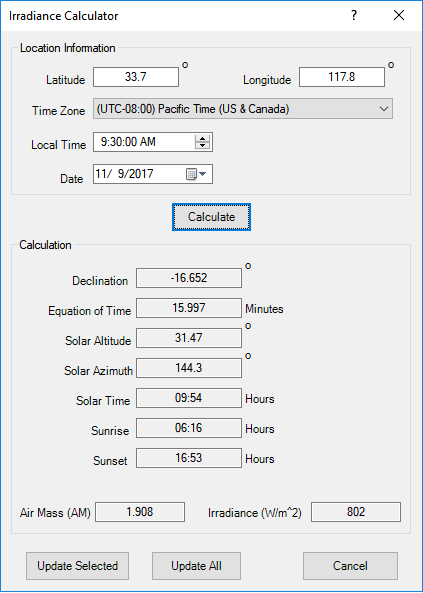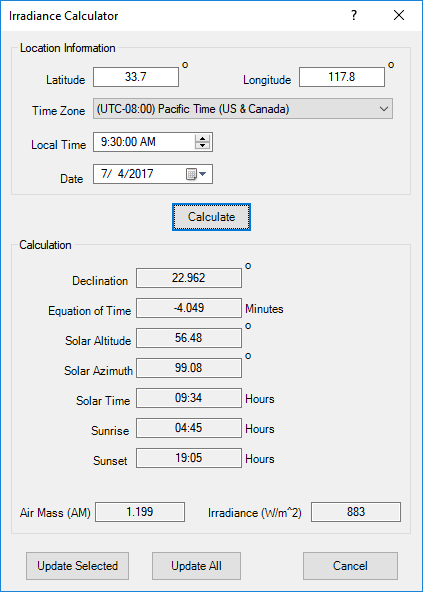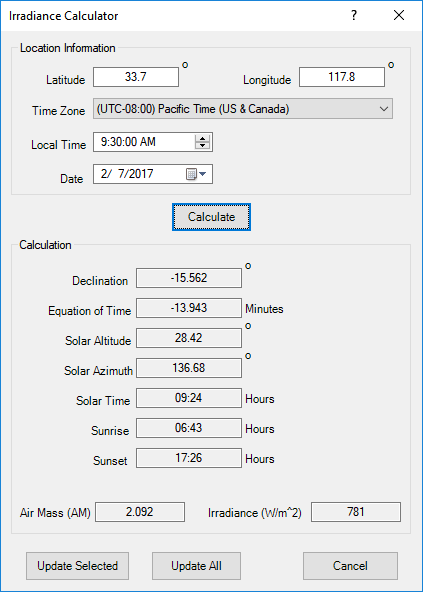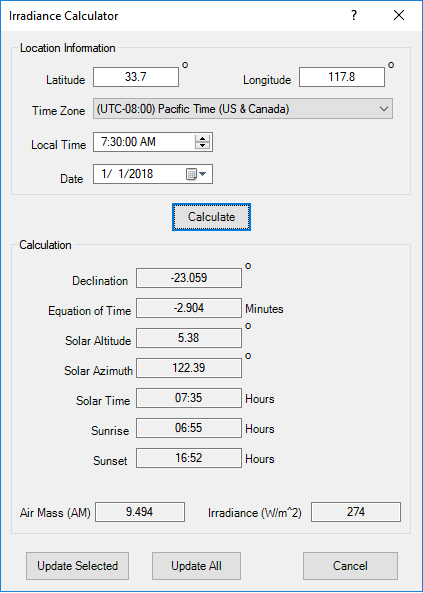
Solar Irradiance Calculator
Photovoltaic array element includes a built-in Solar Irradiance Calculator based on sun position to estimate solar irradiance incident upon a location. Solar Irradiance is the power per unit area available at a location due to solar radiation..
ETAP Solar irradiance calculator is especially useful when designing or estimating electrical power output from the panels without knowledge of the entire network.
- Model and simulate HVDC response under steady-state and transient conditions
HVDC Link
HVDC Transmission Link
Model and Simulate High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission Link and Converter TechnologiesETAP HVDC Transmission Link provides capabilities to simulate and analyze AC/DC electrical power grids.

The integrated modeling of the HVDC Link is utilized to analyze steady-state and dynamic behavior of AC/DC transmission networks, such as optimal power plows, contingency, short-circuit, harmonics, protection, selectivity, and transient stability studies.
The HVDC link includes multiple control schemes and dynamic models for:
- Rectification Station
- Inversion Station
- DC Grid
- AC/DC Coupling Controls
HVDC Link Key Features
- HVDC converter technology model types:
- Voltage Source Converter, VSC
- Current Source Converter, CSC
- Line Commutated Converter, LCC
- Built-in detailed rectifier & inverter dynamic modeling
- Combination of AC-DC & DC-AC conversion operation
- Built-in control schemes
- Inclusive transformer models
- Easy-to-use integrated model
- Accurate steady-state & dynamic modeling
- Unified AC & DC solution in a single study
- IEEE Std 1378 – IEEE Guide for Commissioning High-Voltage Direct-Current (HVDC) Converter Stations and Associated Transmission Systems


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.